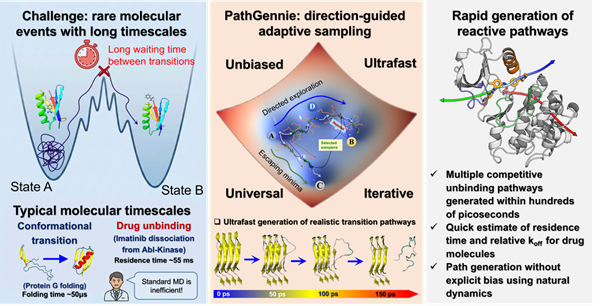
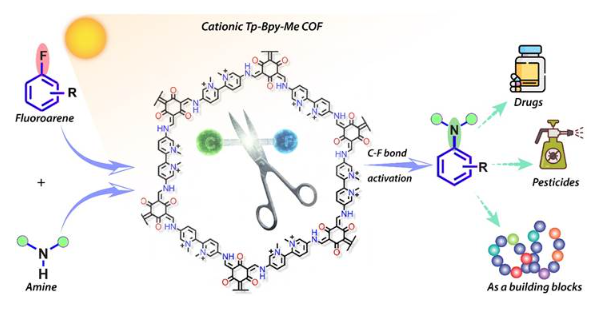
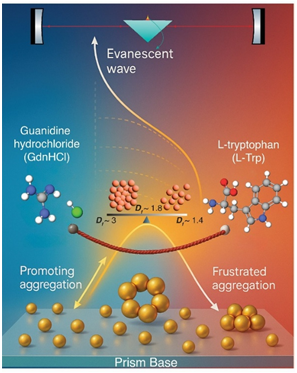
Research
Collaborations
S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences
The S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences is an autonomous research institute engaged in research in basic sciences. The institute was founded under Department of Science and Technology, Government of India in 1986 as a Registered Society. The Centre was established to honour the life and work of Professor S. N. Bose who was a colossal in theoretical physics and has made some of the most fundamental conceptual contributions in the development of Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Statistics. The Centre has emerged as a major institution for research and development in Basic Sciences.